How Microsegmentation Prevents Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware remains one of the most disruptive and financially damaging cyber threats facing organizations of all sizes. Once inside a network, it spreads laterally—encrypting files, databases, applications, and even backups. Traditional flat networks make this lateral movement far too easy.
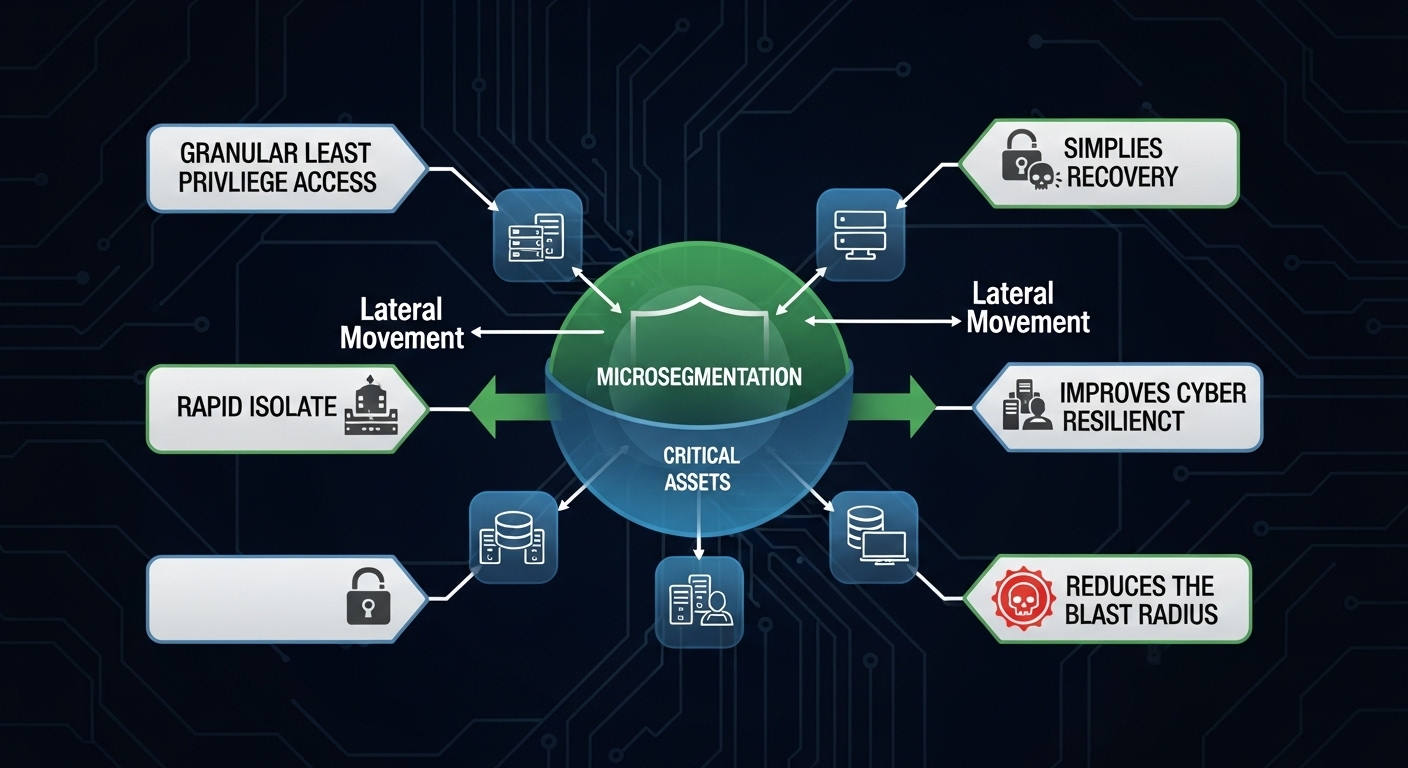
Microsegmentation changes that dynamic. By isolating critical assets, enforcing least-privilege access, and enabling rapid isolation, organizations can contain ransomware before it escalates into a full-scale breach.
Below, we break down how microsegmentation prevents ransomware attacks and strengthens overall cyber resilience.
1. Isolate Critical Assets
Microsegmentation allows organizations to isolate their most sensitive systems—finance servers, domain controllers, and databases—into hardened zones separated from the rest of the corporate network. This isolation ensures ransomware cannot freely move between workloads.
- Identify crown jewels: Conduct a full risk assessment to classify high-value assets for isolation.
- Create hardened zones: Place critical systems in dedicated, locked-down network segments with tightly controlled ingress and egress points.
- Restrict access: Allow only authorized systems or jump hosts to communicate with these zones; block everything else.
- Monitor traffic: Flag and investigate any lateral connections targeting these protected zones.
By proactively segmenting critical systems, organizations drastically reduce the likelihood that ransomware can reach the data that matters most.
2. Limit Lateral Movement
Once ransomware enters a network, its success depends on its ability to move laterally. Microsegmentation blocks that path, enforcing strict controls over east-west traffic.
- Restrict east-west traffic: Control which internal workloads can talk to each other using software-defined perimeters.
- Deny by default: Only explicitly allowed traffic flows between segments—everything else is automatically denied.
- Application-aware policies: Limit communication not only by IP or port but also by application and service.
- Authenticate users and devices: Integrate identity and posture checks to ensure only verified sources move laterally.
- Monitor flows continuously: Alert on any unauthorized connection attempts between segments.
This compartmentalization ensures that even if ransomware compromises one endpoint, it cannot traverse the entire network.
3. Enforce Granular Least-Privilege Access
Microsegmentation supports least-privilege access at the network layer, limiting communication to only what is strictly necessary. This drastically reduces the ransomware attack surface.
- Analyze data flows: Map legitimate traffic between workloads to define only essential communication paths.
- Apply strict ACLs: Explicitly allow required traffic and automatically deny everything else.
- Refine over time: Continuously monitor access patterns and tighten rules as visibility improves.
- Mask critical assets: Hide IPs or ports for sensitive systems using jump hosts or proxies.
- Integrate NAC: Use network access control to validate device compliance before granting any access.
With these fine-grained controls, even sophisticated ransomware campaigns struggle to move or communicate across zones.
4. Enable Rapid Isolation and Containment
When ransomware is detected, speed of containment determines the extent of damage. Microsegmentation enables administrators to instantly isolate compromised workloads or network zones—stopping the infection from spreading.
- Automate isolation: Use orchestration or APIs to cut off affected segments with a single command.
- Define playbooks: Document step-by-step incident response procedures for isolating infected areas.
- Use quarantine zones: Redirect compromised systems to dedicated analysis or remediation segments.
- Validate clean backups: Confirm recovery points for impacted workloads before taking them offline.
- Gain time: Isolation provides critical minutes or hours for security teams to reset credentials and contain further risk.
Microsegmentation transforms response from reactive cleanup to proactive containment.
5. Simplify Recovery
When critical systems and backups are already segregated in secure zones, recovery becomes faster, cleaner, and more predictable. Microsegmentation allows organizations to restore operations without rebuilding entire infrastructures.
- Maintain recent, verified backups of each isolated zone.
- Store backups offline or in secure, access-restricted repositories.
- Focus defense resources on fewer, high-value assets.
- Reduce dependence on full backups.